今天的內容將延續 上一篇 文章中 Operation Process 裡的 3. ,同時我們會非常深入地去解析實現整個 transform function 的程式碼邏輯,對 Operation 的運作流程還不熟悉的讀者們,筆者建議先回頭看完上一篇的內容後再接著繼續閱讀本篇的內容。
我們在 Day18 介紹 Slate 如何使用 Immer.js 時有先簡單提到這個 transform function 過,再丟一次 code 的內容幫讀者回憶一下:
export const GeneralTransforms: GeneralTransforms = {
/**
* Transform the editor by an operation.
*/
transform(editor: Editor, op: Operation): void {
editor.children = createDraft(editor.children)
let selection = editor.selection && createDraft(editor.selection)
try {
selection = applyToDraft(editor, selection, op)
} finally {
editor.children = finishDraft(editor.children)
if (selection) {
editor.selection = isDraft(selection)
? (finishDraft(selection) as Range)
: selection
} else {
editor.selection = null
}
}
},
}
transform function 的內容存放在 transforms/general.ts 這個 file 裡面,跟其他 Transform methods 一起放在同一個 transforms/directory 底下。
這個 method 做的事情本身不多,主要就是將 editor 底下的 children 與 selection 丟入 Immer 的 createDraft 製作 Draft-State ,並在整個運算結束以後執行 finishDraft 而已。
主要的運算工作都是透過 applyToDraft 來執行,所以 ... 是的!我們今天會把所有的精力都放在這個 function 上,那麼以下就~正文開始!
applyToDraft這個 function 基本上就是由一連串的 Switch case 所組成不同的 Operation type 執行不同的運算內容,並在最後回傳計算完的 selection 。
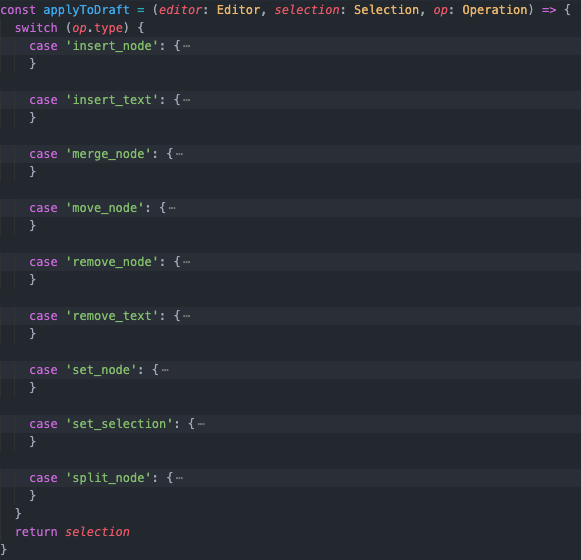
我們就照著圖片上的順序一一介紹吧!
insert_node『插入節點』
先判斷欲 insert 的 node 路徑的最後一個值是否大於它的 parent node 的 children 數量,若大於則代表此路徑超過了同一層 nodes 最尾端的 index ,因而是個不合法的操作
const { path, node } = op
const parent = Node.parent(editor, path)
const index = path[path.length - 1]
if (index > parent.children.length) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot apply an "insert_node" operation at path [${path}] because the destination is past the end of the node.`
)
}
若小於或等於則直接 insert 進指定的位置:
parent.children.splice(index, 0, node)
接著透過 Range.points method Iterate anchor 與 focus point ,再丟入 Point.transform 轉換:
if (selection) {
for (const [point, key] of Range.points(selection)) {
selection[key] = Point.transform(point, op)!
}
}
insert_text『插入文字節點』
如果要被 insert 的 text 為空值則直接 break 此次的 transform
const { path, offset, text } = op
if (text.length === 0) break
將 path 丟入 Node.leaf method 確保它是一個合法的 Text node
const node = Node.leaf(editor, path)
/** 順便附上 Node.leaf method 內容 */
// node.ts
/**
* Get the node at a specific path, ensuring it's a leaf text node.
*/
leaf(root: Node, path: Path): Text {
const node = Node.get(root, path)
if (!Text.isText(node)) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot get the leaf node at path [${path}] because it refers to a non-leaf node: ${node}`
)
}
return node
}
結束事前的判斷程序以後再將字串組在一起 &賦值
const before = node.text.slice(0, offset)
const after = node.text.slice(offset)
node.text = before + text + after
最後跟 insertNode 一樣對 selection 做一模一樣的操作,程式碼是一樣的我們就直接略過了。
merge_node『合併節點』
它的做法是將 operation 裡給定的 path 指向的 node 與它的『前一個 sibling node 合併』。
首先取得 path 指向的 node 資料、前一個 sibling node 資料、 parent node 資料以及 path 指向的 node 的 index
const { path } = op
const node = Node.get(editor, path)
const prevPath = Path.previous(path)
const prev = Node.get(editor, prevPath)
const parent = Node.parent(editor, path)
const index = path[path.length - 1]
接著判斷它們可否合併,只有『同時為 Text node 』與『同時不為 Text node 』這兩種情形可以進行合併。前者將兩組字串合併在一起,後者則是將兩個 Node 的 children 合併在一起
if (Text.isText(node) && Text.isText(prev)) {
prev.text += node.text
} else if (!Text.isText(node) && !Text.isText(prev)) {
prev.children.push(...node.children)
} else {
throw new Error(
`Cannot apply a "merge_node" operation at path [${path}] to nodes of different interfaces: ${node} ${prev}`
)
}
然後再拔掉 path 指向的 node value
parent.children.splice(index, 1)
最後跟 insertNode 一樣對 selection 做一模一樣的操作,程式碼是一樣的我們就直接略過了。
move_node『移動節點』
與字面上的意思一樣,做的事情就是將節點舊的 path 移動到新的 path 。
首先先避開『舊路徑為新路徑的祖先』這個可能性並取得節點、父節點、 index 等資料:
const { path, newPath } = op
if (Path.isAncestor(path, newPath)) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot move a path [${path}] to new path [${newPath}] because the destination is inside itself.`
)
}
const node = Node.get(editor, path)
const parent = Node.parent(editor, path)
const index = path[path.length - 1]
接著是更新節點資料的部分,因為在異動了原始的節點資料後會導致傳入的 path 資料過期而變得不可用,所以這邊的做法是取得 transform 後的新 path 以後再取得這個新 path 的父節點以及新的 index 資料,然後再對這些取得的新資料進行操作,而不是直接操作傳入的 newPath 資料
// This is tricky, but since the `path` and `newPath` both refer to
// the same snapshot in time, there's a mismatch. After either
// removing the original position, the second step's path can be out
// of date. So instead of using the `op.newPath` directly, we
// transform `op.path` to ascertain what the `newPath` would be after
// the operation was applied.
parent.children.splice(index, 1)
const truePath = Path.transform(path, op)!
const newParent = Node.get(editor, Path.parent(truePath)) as Ancestor
const newIndex = truePath[truePath.length - 1]
newParent.children.splice(newIndex, 0, node)
最後跟 insertNode 一樣對 selection 做一模一樣的操作,程式碼是一樣的我們就直接略過了。
remove_node『刪除節點』
刪除節點本身的操作非常的基本,就是直接透過 Array 的 splice method 來達成而已:
const { path } = op
const index = path[path.length - 1]
const parent = Node.parent(editor, path)
parent.children.splice(index, 1)
主要的內容都集中在處理 selection 的更新上,因為刪除的節點有可能是 selection 裡的 anchor 或 focus point 。
這邊的作法是:
selection 裡的 anchor 與 focus pointop.path 『之前』或是『之後』的文字節點selection point 更新為該節點的最後一個字,如果是『之後』的就更新為該節點的第一個字,都沒找到就直接將 selection 設為 null
// Transform all of the points in the value, but if the point was in the
// node that was removed we need to update the range or remove it.
if (selection) {
for (const [point, key] of Range.points(selection)) {
const result = Point.transform(point, op)
if (selection != null && result != null) {
selection[key] = result
} else {
let prev: NodeEntry<Text> | undefined
let next: NodeEntry<Text> | undefined
for (const [n, p] of Node.texts(editor)) {
if (Path.compare(p, path) === -1) {
prev = [n, p]
} else {
next = [n, p]
break
}
}
if (prev) {
point.path = prev[1]
point.offset = prev[0].text.length
} else if (next) {
point.path = next[1]
point.offset = 0
} else {
selection = null
}
}
}
}
remove_text『移除節點內的文字』
因為是操作同一個節點內的文本內容所以很基本,就是取得字串後組合而已。
const { path, offset, text } = op
if (text.length === 0) break
const node = Node.leaf(editor, path)
const before = node.text.slice(0, offset)
const after = node.text.slice(offset + text.length)
node.text = before + after
最後跟 insertNode 一樣對 selection 做一模一樣的操作,程式碼是一樣的我們就直接略過了
set_node『設定節點屬性』
它會擋掉對 root node 的節點屬性設定、對 children 或 text 等主要資料的設定
const { path, properties, newProperties } = op
if (path.length === 0) {
throw new Error(`Cannot set properties on the root node!`)
}
const node = Node.get(editor, path)
for (const key in newProperties) {
if (key === 'children' || key === 'text') {
throw new Error(`Cannot set the "${key}" property of nodes!`)
}
// ...
}
剩下的就是實作邏輯了, 屬性 value 為 null ,或是原本有這項屬性但更新後卻沒有的話,會刪掉節點裡的這項屬性,否則會直接賦值到指定的屬性上
for (const key in newProperties) {
// ...
const value = newProperties[key]
if (value == null) {
delete node[key]
} else {
node[key] = value
}
}
// properties that were previously defined, but are now missing, must be deleted
for (const key in properties) {
if (!newProperties.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
delete node[key]
}
}
set_selection『設定 selection 屬性』
功能很直觀,裡頭的程式碼主要也都是處理一些 edge cases ,例如: selection 原本為 null 的話,新設定的屬性內容必須符合一個合法的 Range type 該有的 properties ,以及不能將 anchor 、 focus 的 value 設為 null 等等
case 'set_selection': {
const { newProperties } = op
if (newProperties == null) {
selection = newProperties
} else {
if (selection == null) {
if (!Range.isRange(newProperties)) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot apply an incomplete "set_selection" operation properties ${JSON.stringify(
newProperties
)} when there is no current selection.`
)
}
selection = { ...newProperties }
}
for (const key in newProperties) {
const value = newProperties[key]
if (value == null) {
if (key === 'anchor' || key === 'focus') {
throw new Error(`Cannot remove the "${key}" selection property`)
}
delete selection[key]
} else {
selection[key] = value
}
}
}
break
}
split_node『拆分節點』
就是一個將節點一分為二的功能,唯一的限制是不能對 Editor 做拆分
const { path, position, properties } = op
if (path.length === 0) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot apply a "split_node" operation at path [${path}] because the root node cannot be split.`
)
}
將基本的資料取出來設為變數以後,會接著區分出 Text node 與 Element node 。
前者會對節點內的字串做操作:
const node = Node.get(editor, path)
const parent = Node.parent(editor, path)
const index = path[path.length - 1]
let newNode: Descendant
if (Text.isText(node)) {
const before = node.text.slice(0, position)
const after = node.text.slice(position)
node.text = before
newNode = {
...(properties as Partial<Text>),
text: after,
}
}
後者則是對 children node 做操作:
else {
const before = node.children.slice(0, position)
const after = node.children.slice(position)
node.children = before
newNode = {
...(properties as Partial<Element>),
children: after,
}
}
然後將新生成的 newNode 塞進對應的位置:
parent.children.splice(index + 1, 0, newNode)
最後跟 insertNode 一樣對 selection 做一模一樣的操作,程式碼是一樣的我們就直接略過了。
呼~一個接著一個介紹,總算是迎來尾聲了。
雖說這篇介紹的 transform function 是 Slate 主要用於處理 Slate node tree 的資料更新的,但我們同時也能發現其實還是有部分的邏輯是被拆到其他的 function 去處理的。
也就是針對『 Location types 』更新的內容,只要是諸如 selection 的 point 更新,或是 path 更新等等的功能都是交由各自對應到的 type 的 transform method api 來處理( Point.transform 、 Path.transform )
下一篇我們就會將目光聚焦在這些 methods 上,來看看在這裡頭又是如何更新 Location type 的內容的。
明天見各位~
